
Traditional data warehouses are nothing if not mature. The added advantage now, ten years later, is that the tools used in conjunction with data lakes have matured and expanded, unlocking all kinds of capabilities – without sacrificing openness. We could tolerate some of the early technical shortcomings because of the openness and cost control we gained.
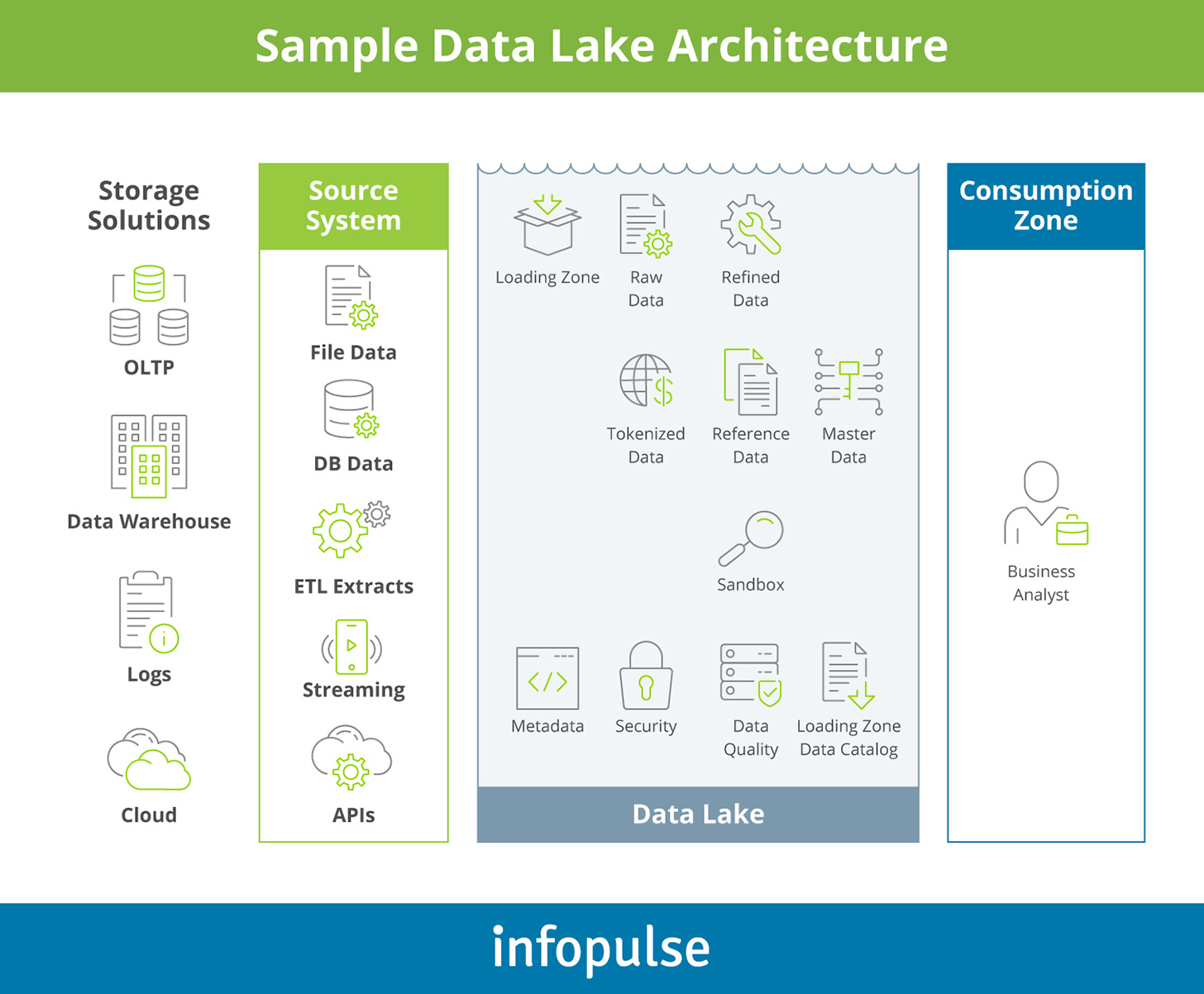
He argued that one of the reasons data lakes were so appealing at the start is that they championed openness. Our advocate for data lake architectures was Aaron Colcord, Senior Director, Data Analytics Engineering at Northwestern Mutual. Before I get to that, though, I’d like to pass on a few key insights from the discussion about what companies ultimately value from these solutions: Maturity Or will the winner be something we haven’t yet imagined?Īt the end of the discussion, we asked our audience to weigh in, and the results were surprisingly clear. Will one of these three concepts prevail? Ultimately, we were trying to determine what the best architecture will be going forward. In early February, I had the chance to host a fun debate on data lake, data warehouse or the data lakehouse with proponents of each architecture at Datanova 2021, Starburst’s annual conference. Now, to add to that, we have this increasingly popular lakehouse concept, which can potentially string together the best of both worlds. More and more companies are shifting toward data lakes, yet the traditional data warehouse continues to provide value, as it has for decades. Migration from traditional architecture: can be very expensive to migrate from data warehouse or data lake to data lakehouse.This is a crazy and slightly confusing time in the data architecture space.Immature technology: Data lakehouse is a fairly new technology and will probably need optimisation.Reduced data redundancy: providing a single all-purpose data storage platform to cater to all business data demands, data lakehouses reduce data duplication.Additionally, providing a single solution, data lakehouses eliminate the costs and time of maintaining multiple data storage systems Low cost: utilize low-cost object storage solutions.At the same time, raw data enables advanced analytics and machine learning Support of BI or ML cases: enabled advanced analytics by providing integration with BI tools.Poor support of BI cases: if data lakes are not properly managed, integration with business intelligence and analytics tools can be difficult.Ī data lakehouse is, as the name suggests, a combination of the best features of both data warehouses and data lakes.ĭata (structured, semi-structured, and unstructured) can be stored in a single location and enables best-in-class machine learning, business intelligence, and streaming capabilities.Support for analytics (AI&ML): storing the data in an open, raw format allows for more sophisticated analytics and usage of various machine and deep learning algorithms.Cost savings: large volumes of data can be stored at very low cost.Allowing the data to remain in its native format allows for more data for analysis and caters to future data use cases Flexible: data lakes allow storing data in any format.When the data is needed, it can be pulled out from the storage and processed for a particular purpose Unlike data warehouses, which store relational data already “cleaned”, a data lake stores data using a flat architecture and object storage in its raw form.

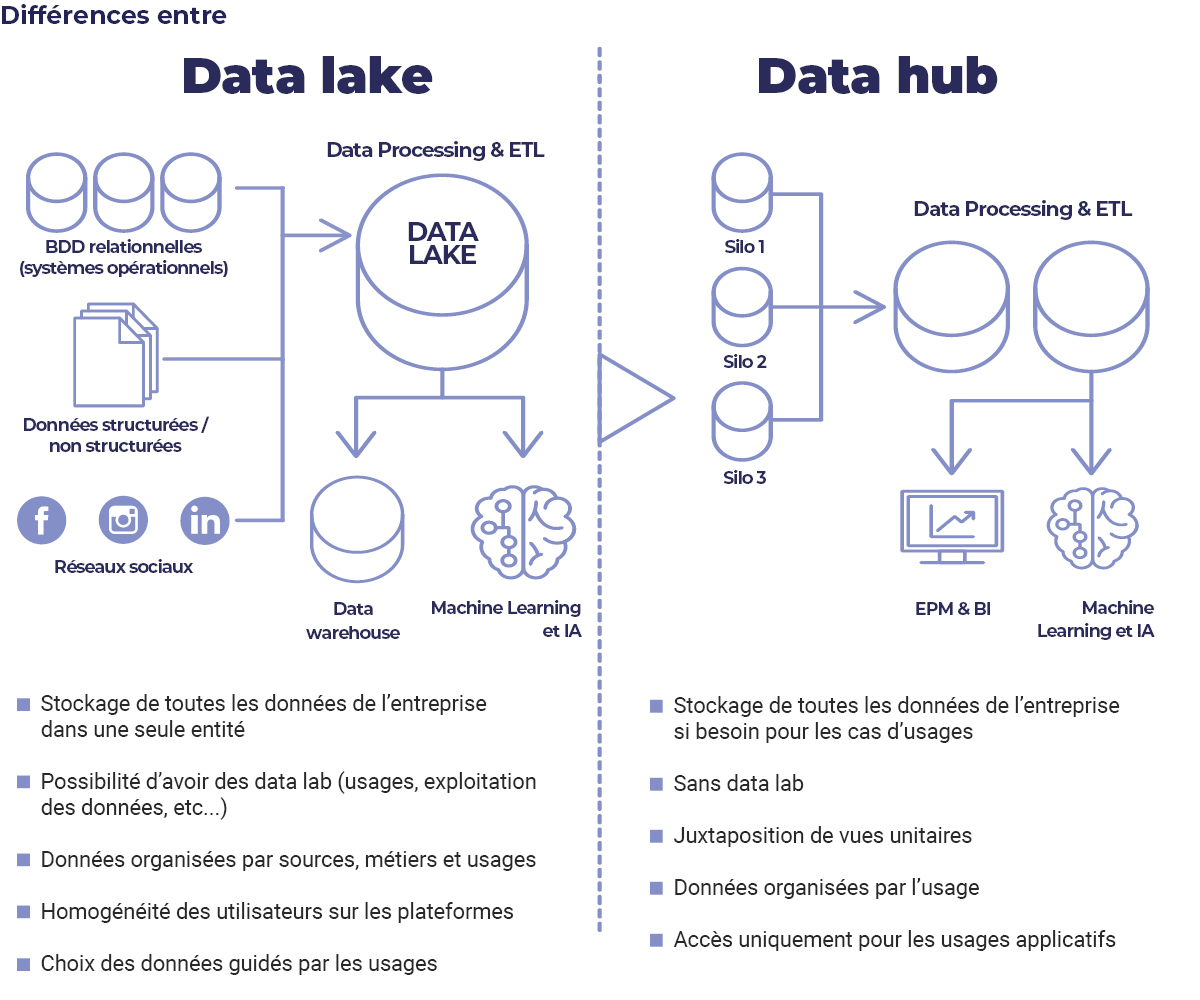
High maintenance cost: Data warehouses can be expensive to implement and maintain.Ī data lake is a centralized storage repository with high flexibility that stores large amounts of structured and unstructured data in its original, and unformatted form.Not Flexible: Data warehouses work well with structured data but aren’t meant to work with unstructured data.Easy access to data: to start using the data for their purposes, the teams have to do little to no preparations as all the data is already transformed.High Quality of data: certified data, single source of 'truth of data'.Improved reporting: provide institutional reporting (more or less interactive) but also give end-users the possibility to conduct their own analysis.Data engineers and analysts can extract data from data warehouses using SQL clients, business intelligence tools, and other applications. A data warehouse can improve business operational efficiency by allowing users to quickly access historical information on key business metrics. A data warehouse represents a single source of 'truth of data' in an organization and serves as a central component of business reporting and analysis. A data warehouse is a structured data repository for storing large amounts of information from internal and external sources.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
